https://github.com/InguChoi/RANSAC
GitHub - InguChoi/RANSAC: RANSAC Python Version
RANSAC Python Version. Contribute to InguChoi/RANSAC development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
직선
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
# RANSAC 2D Class
class RANSAC_2D_Class:
def __init__(self, iter_max, offset):
self.iter_max = iter_max
self.offset = offset
self.inputData = list()
self.inliner_max = 0
self.ransac_line = list()
self.time = np.linspace(0, 100, 100)
def setData(self, inputData):
self.inputData = inputData
def getRANSAC(self):
return self.ransac_line
# Select the points randomly
def selectPoints(self):
self.selectPoint = random.sample(self.inputData, 2)
def makeHypothesisLine(self):
point1 = list()
point2 = list()
# Process the equation
for i, data in enumerate(self.inputData):
if(data == self.selectPoint[0]):
point1 = [i, data]
if(data == self.selectPoint[1]):
point2 = [i, data]
# y = ax + b
inclination = (point2[1] - point1[1]) / (point2[0] - point1[0])
b = point1[1] - inclination*point1[0]
hyp_line = (inclination * self.time) + b
# y = ax + b + offset
# y = ax + b - offset
hyp_line_up = (inclination * self.time) + b + self.offset
hyp_line_down = (inclination * self.time) + b - self.offset
# Calculate the number of the inliner counts
inliner_cnt = 0
for i in range(len(hyp_line)):
if((hyp_line_up[i] > self.inputData[i]) and (hyp_line_down[i] < self.inputData[i])):
inliner_cnt = inliner_cnt + 1
# Calculate the maximum inliner counts for finding the best model
if(self.inliner_max < inliner_cnt):
self.inliner_max = inliner_cnt
self.ransac_line = hyp_line
def processRANSAC(self):
for iteration in range(self.iter_max):
self.selectPoints()
self.makeHypothesisLine()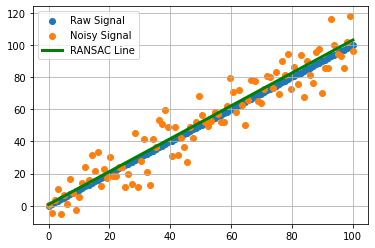
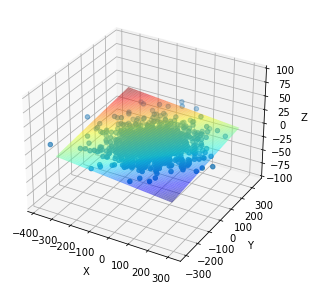
평면
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
import numpy as np
from sklearn import preprocessing
# RANSAC 3D Class
class RANSAC_3D_Class:
def __init__(self, iter_max, offset):
self.iter_max = iter_max
self.offset = offset
self.inliner_max = 0
self.ransac_plane = list()
self.x = 0
self.y = 0
self.z = 0
self.x_select = 0
self.y_select = 0
self.z_select = 0
def setData(self, x, y, z):
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.z = z
def getRANSAC(self):
return self.ransac_plane
# 1. Select the points randomly
def selectPoints(self):
self.x_select = random.sample(self.x.tolist(), 3)
self.y_select = random.sample(self.y.tolist(), 3)
self.z_select = random.sample(self.z.tolist(), 3)
def makeHypothesisPlane(self):
# 2. Plane equation
point1 = np.array([self.x_select[0], self.y_select[0], self.z_select[0]])
point2 = np.array([self.x_select[1], self.y_select[1], self.z_select[1]])
point3 = np.array([self.x_select[2], self.y_select[2], self.z_select[2]])
v12 = point2 - point1
v13 = point3 - point1
n = np.cross(v12, v13)
d = -np.inner(n, point1)
# Plane equation
X = np.arange(-300, 300, 10)
Y = np.arange(-300, 300, 10)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
Z = (-n[0]/n[2] * X) + (-n[1]/n[2] * Y) - d/n[2]
# 3. Calculate the number of the inliner points
inliner_cnt = 0
for i in range(len(z)):
check_z_upper = (-n[0]/n[2] * x[i]) + (-n[1]/n[2] * y[i]) - d/n[2] + self.offset
check_z_lower = (-n[0]/n[2] * x[i]) + (-n[1]/n[2] * y[i]) - d/n[2] - self.offset
if(z[i] < check_z_upper and z[i] > check_z_lower):
inliner_cnt = inliner_cnt + 1
# 4. Find the maximum inliner points
if(self.inliner_max < inliner_cnt):
self.inliner_max = inliner_cnt
self.ransac_plane = Z
def processRANSAC(self):
for iteration in range(self.iter_max):
self.selectPoints()
self.makeHypothesisPlane()